|
Strain Name
|
C57BL/6-Il17atm1(IL17A)Bcgen Il17ftm1(IL17F)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name
|
B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice
|
|
Background
|
C57BL/6
|
Catalog number
|
120554
|
|
Related Genes
|
IL17A (interleukin 17A); IL17F (interleukin 17F)
|
NCBI Gene ID
|
16171,257630
|
Protein expression analysis
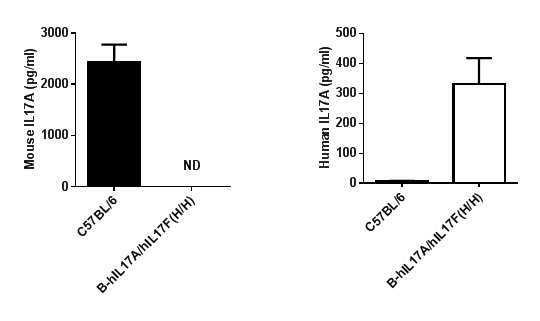
Strain specific IL17A expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice by ELISA.
Serum were collected from wild type (WT) mice and homozygous B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice (H/H) stimulated with anti-mCD3ε and anti-mCD28 antibody in vivo, and analyzed by ELISA with species-specific IL17A ELISA kit. Mouse IL17A was detectable in WT mice. Human IL17A was detectable in homozygous B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice (H/H). ND: not detectable.
Protein expression analysis
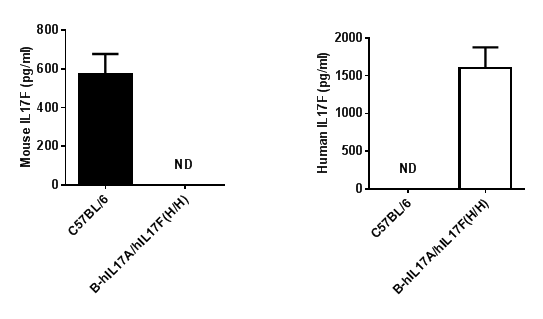
Strain specific IL17F expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice by ELISA.
Naïve CD4+ T cells were sorted from splenocytes of wild type (WT) mice and homozygous B-hIL17A/hIL17F (H/H) mice, and induced into Th17 cells. Th17 cells were stimulated by PMA and lonomycin. The Th17 cells culture supernatants were collected and analyzed by ELISA with species-specific IL17F ELISA kit. Mouse IL17F was detectable in WT mice. Human IL17F was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice (H/H). ND: not detectable.
Analysis of lymph node T cell subpopulations in B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice
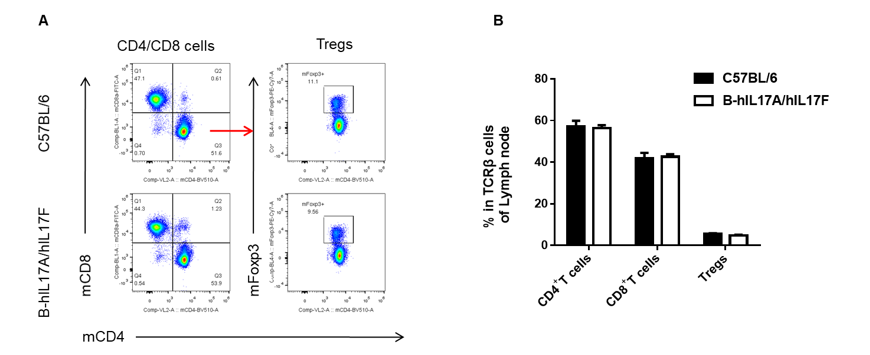
Analysis of lymph node T cell subpopulations by FACS.
Leukocytes were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice (n=3, 7 week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the leukocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for CD3 T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of CD8, CD4, and Treg cells in homozygous B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that introduction of hIL17A/hIL17F in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell sub types in lymph node. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
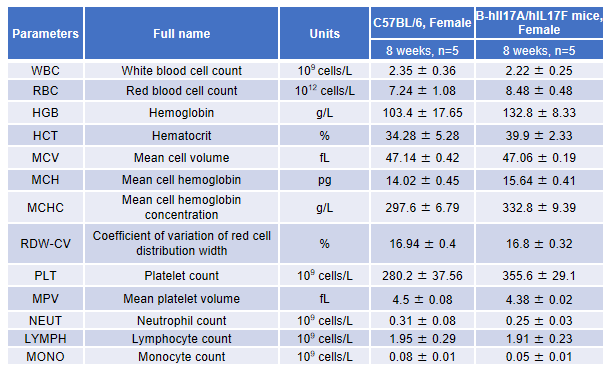
Blood routine test in B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice
Complete blood count (CBC).
Blood from female C57BL/6 and B-hIL17A/hILl7F mice (n=5, 8 week-old) was analyzed for CBC. There was no differences among any measurement between C57BL/6 and B-hIL17A/hILl7F mice, indicating that introduction of hIL17A and hIL17F in place of its mouse counterpart does not change blood cell composition and morphology. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
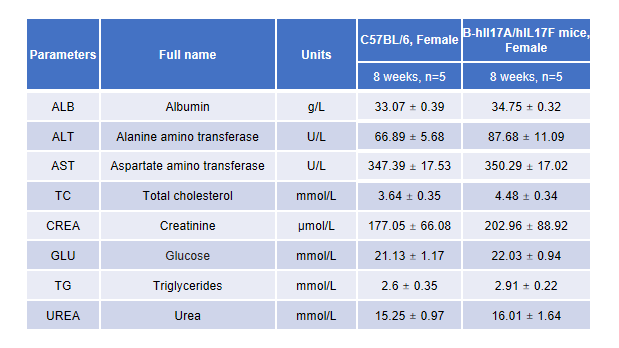
Blood chemistry of B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice
Blood chemistry tests of B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice.
Serum from the C57BL/6 and B-hIL17A/hILl7F mice (n=3, 8 week-old) was analyzed for levels of ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and AST (aspartate aminotransferase). There was no differences on either measurement between C57BL/6 and B-hIL17A/hILl7F mice, indicating that introduction of hIL17A and hIL17F in place of its mouse counterpart does not change ALT and AST levels or health of liver. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Experimental schedule for induction of psoriasis-like skin lesions and in vivo efficacy of anti-human IL17A and IL17F antibody
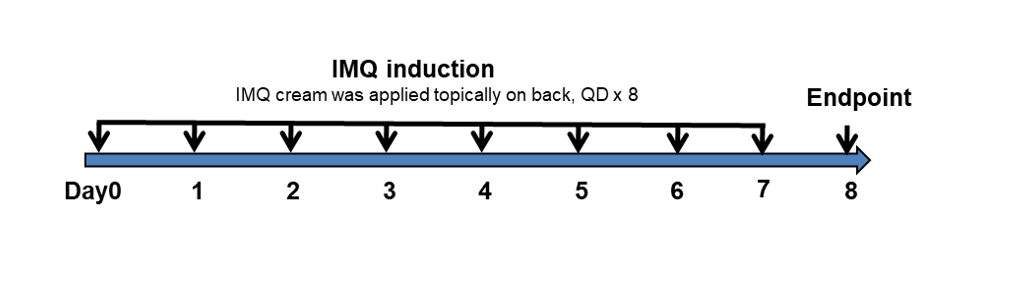
Experimental schedule for induction of psoriasis-like skin lesions in B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice. Mice at 10-12 week-old of age received a daily topical of commercially available IMQ cream on the shaved back for 8 consecutive days to induce psoriasis-like skin lesions. Control mice were treated similarly with vaseline cream. Severity of skin inflammation was daily scored and back skin was collected at the endpoint. IMQ: imiquimod.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human IL17A and IL17F antibody with psoriasis model induced in B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice
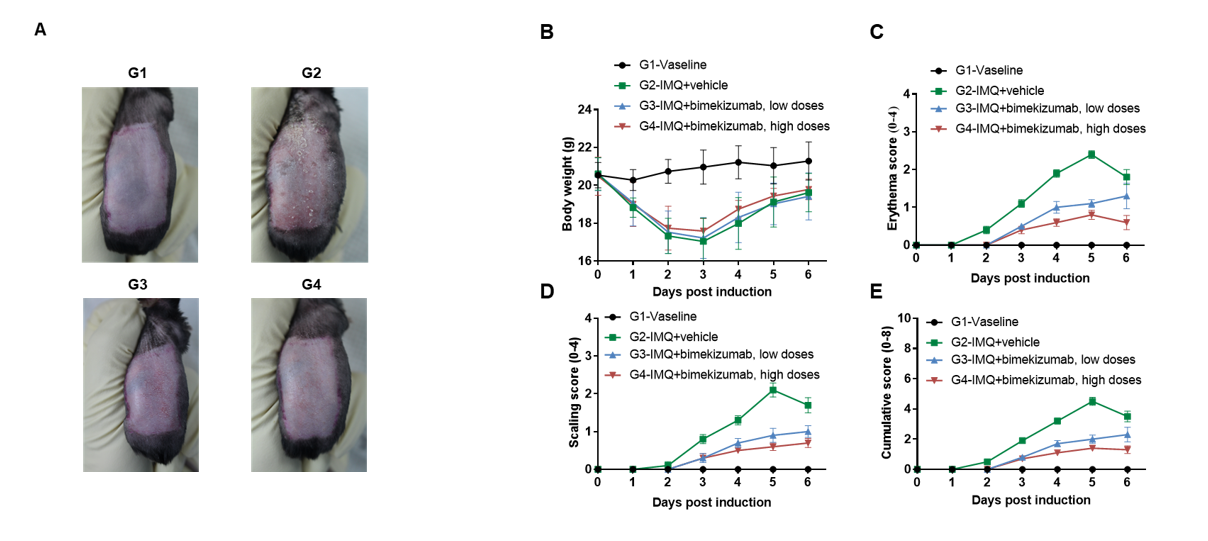
IMQ-induced skin inflammation in B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice phenotypically resembles psoriasis.
Mice (female, 10 week-old, n=5) were scored daily for up to 6 days for body weight and clinical signs of skin inflammation following treatment with imiquimod (IMQ) cream. Mice in each group were treated with different dose of bimekizumab produced in house. Doses are shown in legend. (A) Phenotypical presentation of mouse back skin after 6 days of treatment. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. (C-D) Erythema and scaling score of the back was scored daily on a scale from 0 to 4. Additionally, the cumulative score (erythema plus scaling) is depicted. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human IL17A and IL17F antibody with psoriasis model induced in B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice
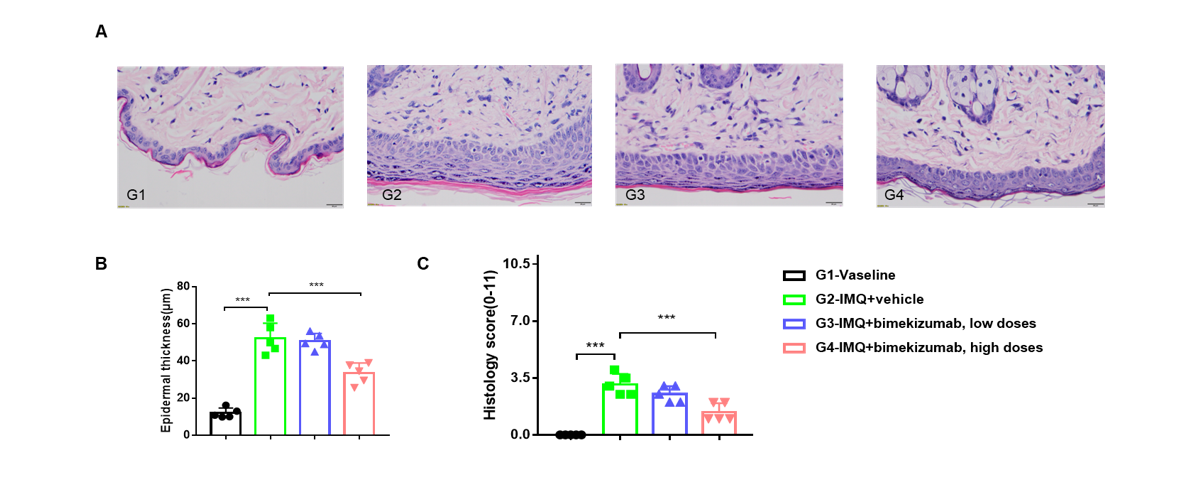
Dose dependent effects of antibody on keratinocyte proliferation and inflammatory cell infiltration in IMQ induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice.
Back skin was collected at the endpoint and stained with Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). (A) H&E staining of the back skin of mice. (B) Epidermal thickness of the mice. (C) Histological changes were scored on a scale from 0 to 11. Results indicated that bimekizumab (in house) significantly reduced psoriasis-like skin lesions in B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice, confirming that B-hIL17A/hIL17F mice is a powerful model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human IL17A and IL17F antibody.