| Strain Name |
C57BL/6N-Il1r1tm2(IL1R1)Bcgen/Bcgen |
Common Name | B-hIL1R1 mice |
| Background | C57BL/6N | Catalog number | 113574 |
|
Aliases |
CD121A, CRMO3, D2S1473, IL-1R-alpha, IL-1RT1, IL1R, IL1RA, P80 | ||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
3554 | ||
- IL1R1 encodes a cytokine receptor that belongs to the interleukin-1 receptor family. The encoded protein is a receptor for interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. It is an important mediator involved in many cytokine-induced immune and inflammatory responses. IL1R1 plays a key role in the immune system and is an important research target in tumors, autoimmune diseases, and central nervous system disorders.
- Gene targeting strategy for B-hIL1R1 mice. A chimeric CDS that encodes human IL1R1 signal peptide and extracellular domain, mouse Il1r1 transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain is inserted right after mouse Il1r1 exon 2 to replace the part of exon 2 to exon 5 of mouse Il1r1 gene. The chimeric IL1R1 protein expression will be driven by endogenous mouse Il1r1 promoter, while mouse Il1r1 gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
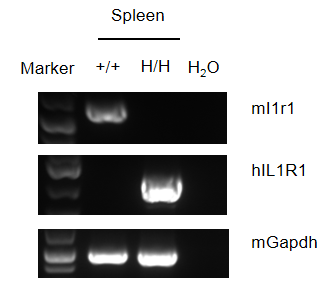
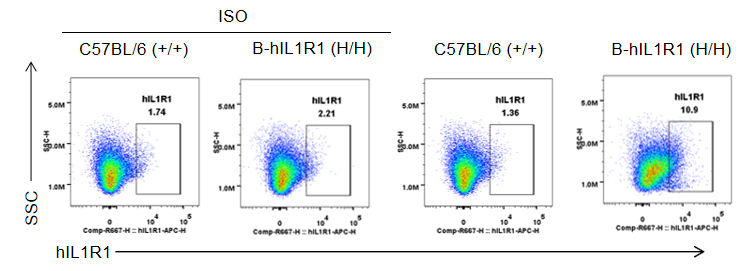
- Human IL1R1 mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hIL1R1 mice. Human IL1R1 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hIL1R1 mice. And IL1B can trigger downstream signaling pathways in B-hIL1R1 mice.
Gene targeting strategy for B-hIL1R1 mice. A chimeric CDS that encodes human IL1R1 signal peptide and extracellular domain, mouse Il1r1 transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain is inserted right after mouse Il1r1 exon 2 to replace the part of exon 2 to exon 5 of mouse Il1r1 gene. The chimeric IL1R1 protein expression will be driven by endogenous mouse Il1r1 promoter, while mouse Il1r1 gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
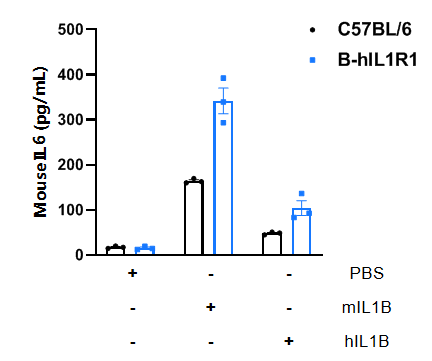
Function analysis of IL1R1 in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hIL1R1 mice by ELISA. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hIL1R1 mice (H/H), and then stimulated with 100 ng/mL mouse IL1B (mIL1B) or human IL1B (hIL1B) for 48 h. Both mIL1B and hIL1B can induce mouse IL-6 production in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hIL1R1 mice. The results indicate that IL1B can trigger downstream signaling pathways in B-hIL1R1 mice.









