B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice
| Strain Name |
C57BL/6-Il2tm1(IL2)Bcgen Il2ratm1(IL2RA)Bcgen ll2rbtm2(IL2RB)Bcgen ll2rgtm2(IL2RG)Bcgen ll15tm1(IL15)Bcgen ll15ratm1(IL15RA)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name |
B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice
|
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number | 112820 |
|
Aliases |
IL-2, TCGF, lymphokine P55, CD25, IL2R, IMD41, TCGFR, IDDM10 CD122, IMD63, IL15RB, P70-75 P64, CIDX, IMD4, CD132, SCIDX, IL-2RG, SCIDX1 IL-15 CD215 |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
3558, 3559, 3560, 3561, 3600, 3601 | ||
- The interleukin-2 (IL2) protein, encoded by the IL2 gene, is a critical cytokine secreted by activated CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes, playing a pivotal role in the proliferation of T and B lymphocytes. The expression of IL2 in mature thymocytes is characterized by monoallelic regulation, representing a distinctive mechanism for the precise control of gene expression. The high-affinity IL2 receptor is composed of the interleukin 2 receptor alpha (IL2RA) and beta (IL2RB) chains, in conjunction with the common gamma chain (IL2RG). Homodimeric configurations of the alpha chains (IL2RA) yield a low-affinity receptor, while the beta chains (IL2RB) in a homodimeric state produce a receptor with medium affinity. Typically, IL2RA is an integral membrane protein; however, a soluble form has been identified and is known to arise from extracellular proteolytic processes. The interleukin-15 (IL15) protein, encoded by the IL15 gene, is a crucial cytokine involved in the regulation of T and natural killer cell activation and proliferation, sharing numerous biological activities with interleukin-2 (IL2). The population of CD8+ memory cells is modulated by a delicate balance between IL15 and IL2. IL15 activates Janus kinase (JAK) kinases and facilitates the phosphorylation and activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3, 5, and 6 (STAT3, STAT5, and STAT6). The IL15 receptor alpha (IL15RA) gene encodes a receptor that binds specifically to IL15 with high affinity. The receptors for IL15 and IL2 share two common subunits, IL2R beta and IL2R gamma, underpinning the overlapping biological activities of these two cytokines. The protein encoded by this gene exhibits structural similarity to IL2R alpha, an additional IL2-specific subunit required for high-affinity IL2 binding. Notably, IL15RA can bind IL15 with high affinity independently of other subunits, implying distinct functional roles for IL15 and IL2.
- The mouse Il2 gene that encodes the full coding sequence was replaced by human IL2 full coding sequence. The mouse Il2ra gene that encodes the extracellular domain was replaced by human IL2RA counterpart gene sequences. The mouse Il2rb gene that encodes the extracellular domain was replaced by human IL2RB counterpart gene sequences. The mouse Il2rg gene that encodes the full coding region sequences was replaced by human IL2RG counterpart gene sequences. The mouse Il15 gene that encodes the full coding sequence was replaced by human IL15 counterpart gene sequences. The mouse Il15ra gene that encodes the extracellular region was replaced by human IL15RA counterpart gene sequences.
- Human IL2, IL2RA, IL2RB, IL2RG, IL15, and IL15RA were exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
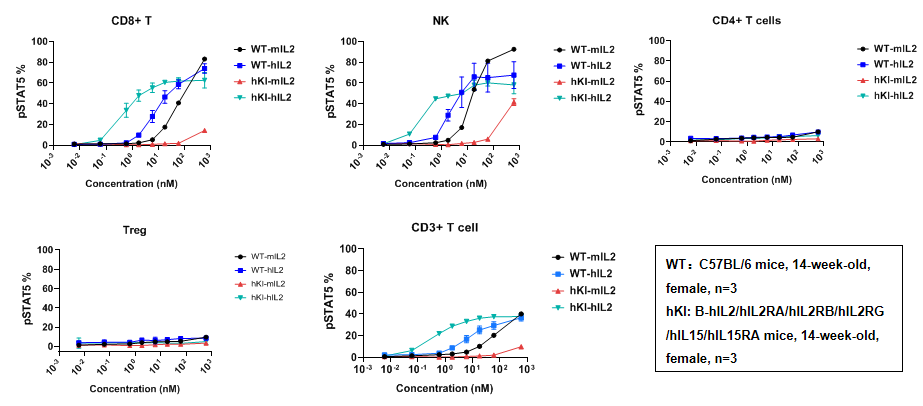
- IL2 induced pSTAT5 in CD8+T cells, CD4+T cells, Tregs, and NK cells in a dose dependent manner in the B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice.
- CHS model: The contact hypersensitivity(CHS) model can be established successfully in the B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice.
- B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of the vitiligo and other autoimmune disease.
- Application: This product is used for pharmacodynamics and safety evaluation of the vitiligo and other autoimmune diseases.
Targeting strategy
- Gene targeting strategy for B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice.
- The exons 1-4 of mouse Il2 gene that encode the whole molecule (ATG to STOP codon) were replaced by human counterparts in B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice. The promoter, 5’UTR and 3’UTR region of the mouse gene are retained. The human IL2 expression is driven by endogenous mouse Il2 promoter, while mouse Il2 gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
- The exons 2-6 of mouse Il2ra gene that encode extracellular domain were replaced by human counterparts in B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice. The genomic region of mouse Il2ra gene that encodes cytoplasmic portion is retained. The promoter, 5’UTR and 3’UTR region of the mouse gene are also retained. The chimeric IL2RA expression is driven by endogenous mouse Il2ra promoter, while mouse Il2ra gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
- The exons 2-8 of mouse Il2rb gene that encode extracellular domain were replaced by human counterparts in B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice. The genomic region of mouse Il2rb gene that encodes cytoplasmic portion is retained. The promoter, 5’UTR and 3’UTR region of the mouse gene are also retained. The chimeric IL2RB expression is driven by endogenous mouse Il2rb promoter, while mouse Il2rb gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
- The exons 1-7 of mouse Il2rg gene that encode signal peptide, extracellular domain, transmembrane domain, cytoplasmic region were replaced by human counterparts in B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice. The promoter and 5’UTR region of the mouse gene are retained. The human IL2RG expression is driven by endogenous mouse Il2rg promoter, while mouse Il2rg gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
- The exons 3-8 of mouse Il15 gene that encode the whole molecule (ATG to STOP codon) were replaced by human counterparts in B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice. The promoter, 5’UTR and 3’UTR region of the mouse gene are retained. The human IL15 expression is driven by endogenous mouse Il15 promoter, while mouse Il15 gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
- The exons 2-6 of mouse Il15ra gene that encode extracellular domain were replaced by human counterparts in B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice. The genomic region of mouse Il15ra gene that encodes cytoplasmic portion is retained. The promoter, 5’UTR and 3’UTR region of the mouse gene are also retained. The chimeric IL15RA expression is driven by endogenous mouse Il15ra promoter, while mouse Il15ra gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
Protein expression analysis of IL2 in serum
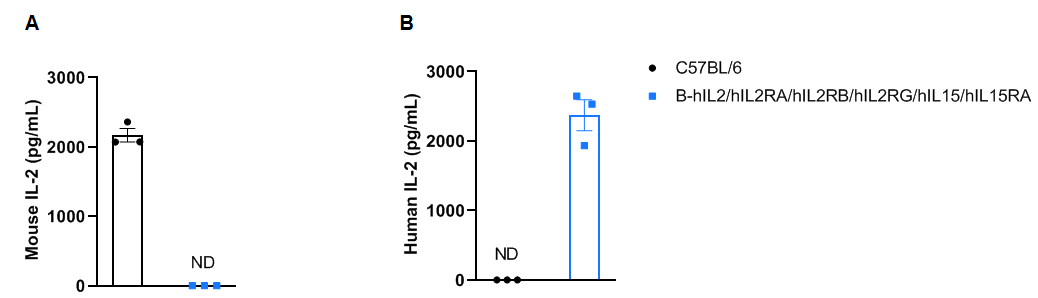
Strain specific IL2 expression analysis in B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice by ELISA. Serum were collected from male wild-type mice C57BL/6 mice (n=3, 6-week-old) and homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice (n=3, 6-week old) stimulated with anti-mCD3ε antibody (7.5 μg/mice) and anti-CD28 antibody (5 μg/mice) in vivo for 3 h, and analyzed by ELISA with species-specific IL2 ELISA kit (mouse IL2: Biolegend, 431004; human IL2: Biolegend, 431804 ). Mouse IL2 was only detectable in wild-type mice (A). Human IL2 was exclusively detectable in homozygous mice but not in wild-type mice (B).
Protein expression analysis of IL2RA in T cells
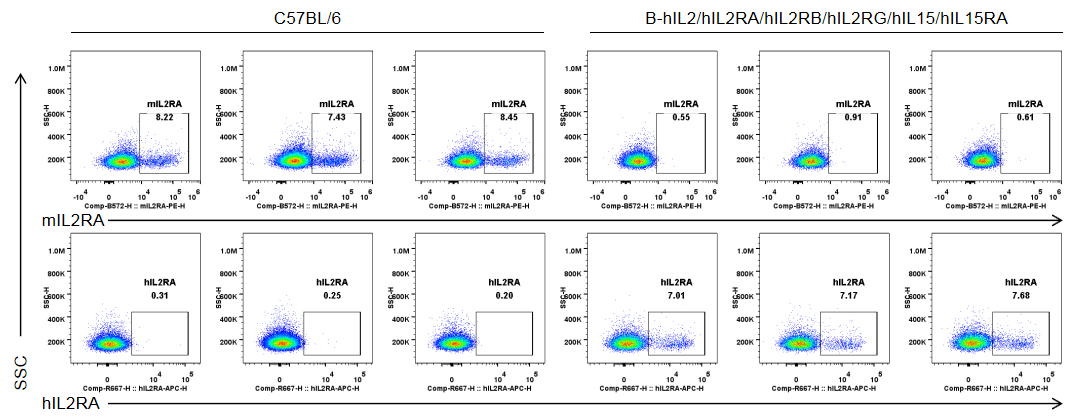
Strain specific IL2RA expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (male, 6-week-old, n=3/group) and homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice (male, 6-week-old, n=3/group) stimulated with anti-CD3ε antibody (7.5 μg/mice, i.p.) and anti-mCD28 antibody (5 μg/mice, i.p.) in vivo for 3 h, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-IL2RA antibody (anti-mIL2RA antibody: Biolegend, 102008. anti-hIL2RA antibody: Biolegend, 302610). mIL2RA was only detectable in wild-type mice, and hIL2RA was exclusively detectable in T cells in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice.
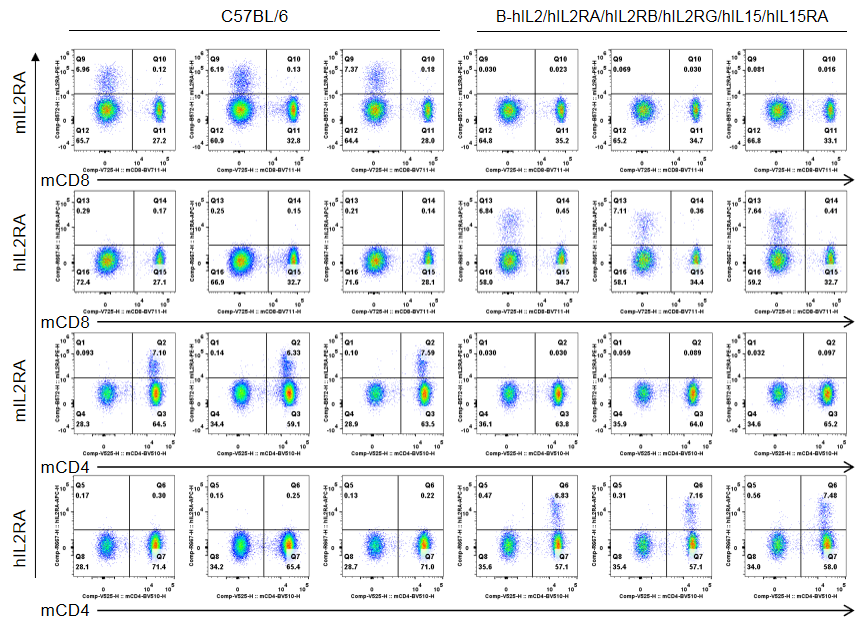
Strain specific IL2RA expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (male, 6-week-old, n=3/group) and homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice (male, 6-week-old, n=3/group) stimulated with anti-CD3ε antibody (7.5 μg/mice, i.p.) and anti-mCD28 antibody (5 μg/mice, i.p.) in vivo for 3 h, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-IL2RA antibody (anti-mIL2RA antibody: Biolegend, 102008. anti-hIL2RA antibody: Biolegend, 302610). mIL2RA was only detectable in wild-type mice, whlie hIL2RA was exclusively detectable in CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice.
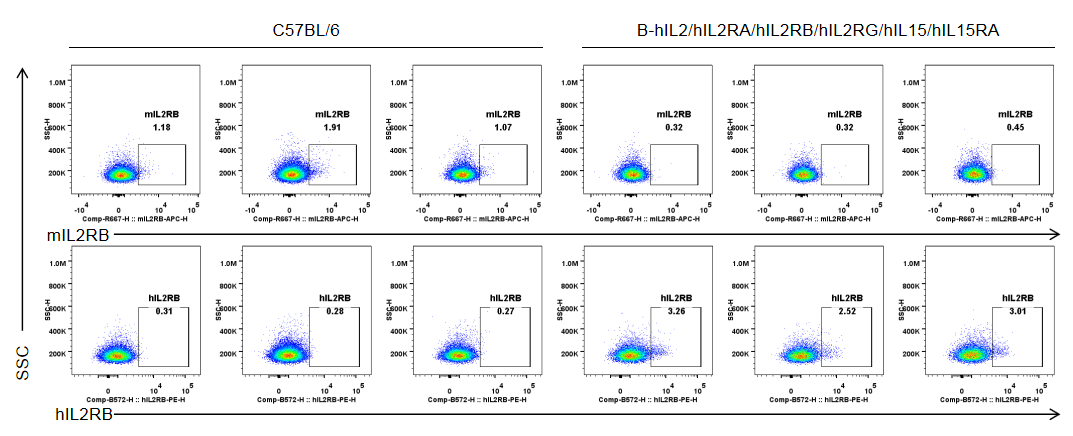
Strain specific IL2RB expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (male, 6-week-old, n=3/group) and homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice (male, 6-week-old, n=3/group) stimulated with anti-CD3ε antibody (7.5 μg/mice, i.p.) and anti-mCD28 antibody (5 μg/mice, i.p.) in vivo for 3 h, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-IL2RB antibody (anti-mIL2RB antibody: Biolegend, 105911. anti-hIL2RB antibody: Biolegend, 339005). mIL2RB was only detectable in wild-type mice, and hIL2RB was exclusively detectable in T cells in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice.
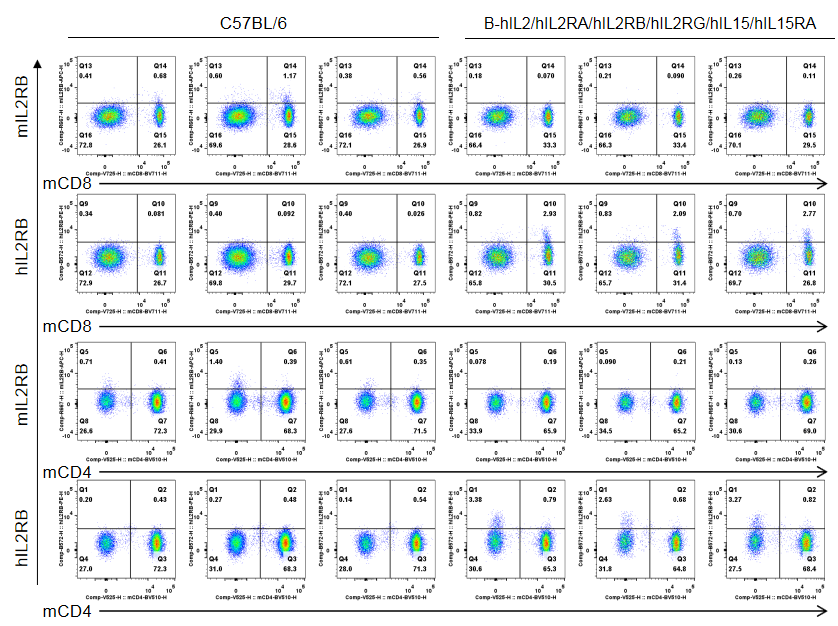
Strain specific IL2RB expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (male, 6-week-old, n=3/group) and homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice (male, 6-week-old, n=3/group) stimulated with anti-CD3ε antibody (7.5 μg/mice, i.p.) and anti-mCD28 antibody (5 μg/mice, i.p.) in vivo for 3 h, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-IL2RB antibody (anti-mIL2RB antibody: Biolegend, 105911. anti-hIL2RB antibody: Biolegend, 339005). mIL2RB was only detectable in wild-type mice, and hIL2RB was exclusively detectable in CD8+ T cells in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice.
Mice used in the experiment: male, 6-week-old, n=3/group.
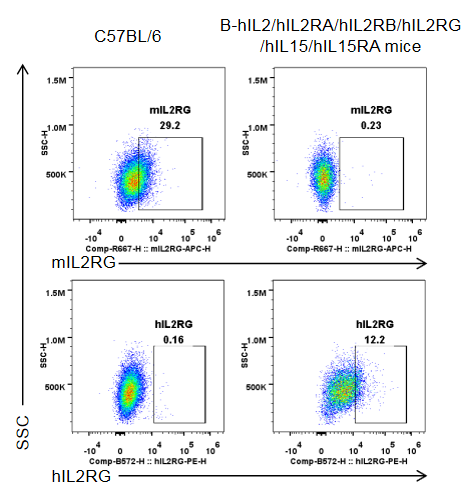
Strain specific IL2RG expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (male, 10-week-old, 1 mice/group) and homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice (male, 10-week-old, 1 mice/group. ), and cultured in 96-well plates pre-coated with 2 μg/mL anti-mCD3ε and 5 μg/mL anti-mCD28 antibody for 24 h, and then cells were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-IL2RG antibody (anti-mIL2RG antibody: Biolegend, 132308. anti-hIL2RG antibody: Biolegend, 338606). mIL2RG was only detectable in wild-type mice, while hIL2RG was exclusively detectable in T cells in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice.
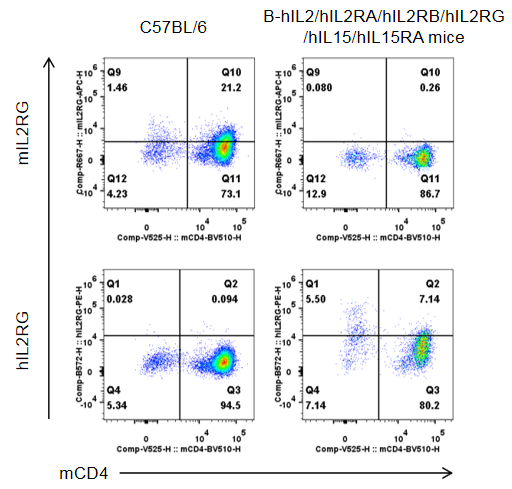
Strain specific IL2RG expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (male, 10-week-old, 1 mice/group) and homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice (male, 10-week-old, 1 mice/group. ), and cultured in 96-well plates pre-coated with 2 μg/mL anti-mCD3ε and 5 μg/mL anti-mCD28 antibody for 24 h, and then cells were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-IL2RG antibody (anti-mIL2RG antibody: Biolegend, 132308. anti-hIL2RG antibody: Biolegend, 338606). mIL2RG was only detectable in wild-type mice, while hIL2RG was exclusively detectable in CD4+T cells in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice.
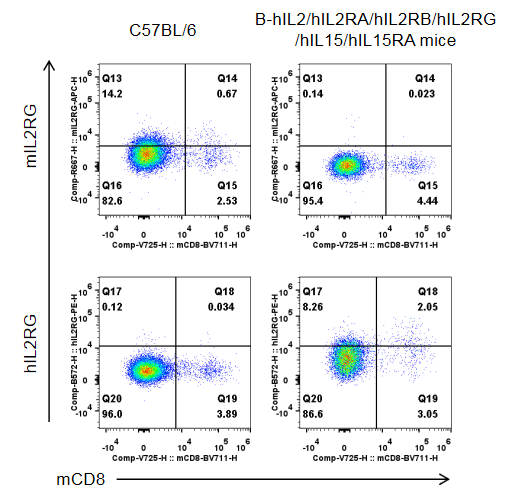
Strain specific IL2RG expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (male, 10-week-old, 1 mice/group) and homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice (male, 10-week-old, 1 mice/group), and cultured in 96-well plates pre-coated with 2 μg/mL anti-mCD3ε and 5 μg/mL anti-mCD28 antibody for 24 h, and then cells were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-IL2RG antibody (anti-mIL2RG antibody: Biolegend, 132308. anti-hIL2RG antibody: Biolegend, 338606). mIL2RG was only detectable in wild-type mice, while hIL2RG was exclusively detectable in CD8+T cells in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice.
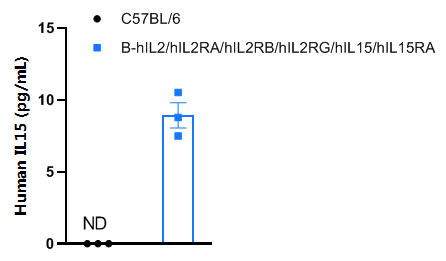
Strain specific IL15 expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice by ELISA. Serum was collected from male wild-type C57BL/6 mice (n=3, 11-week-old) and homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice (n=3, 11-week-old) stimulated with APAP (350 mg/kg mice, i.p.) in vivo for 24 h after starvation for overnight, and analyzed by ELISA with anti-human IL15 ELISA kit (R&D systems, D1500). Human IL15 was exclusively detectable in homozygous mice, but not in wild-type mice.
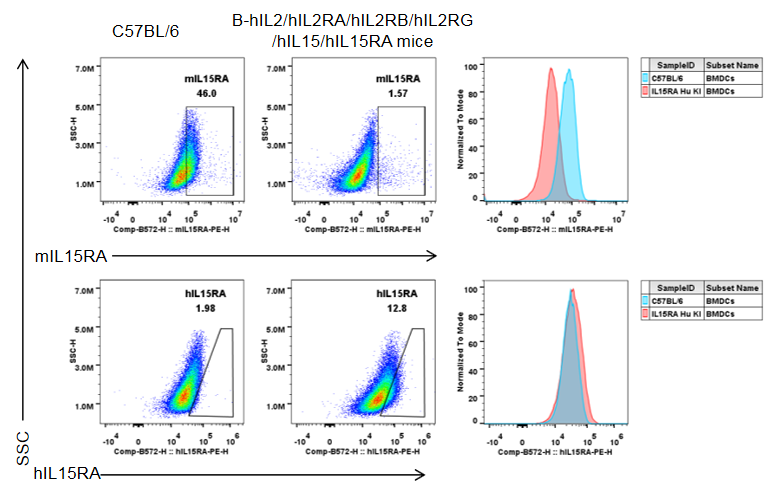
Strain specific IL15RA expression analysis in homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA by flow cytometry. Bone marrow cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice, and cultured in 6-well plates stimulated with GM-CSF and IL-4 for 7 days and LPS (1 μg/mL) for 18 h to induce BMDCs. Then BMDCs were collected and analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-mIL15RA antibody (BD, 568235) and anti-hIL15RA antibody (Biolegend, 330207). mIL15RA was only detectable in wild-type mice. hIL15RA was exclusively detectable in homozygous mice.
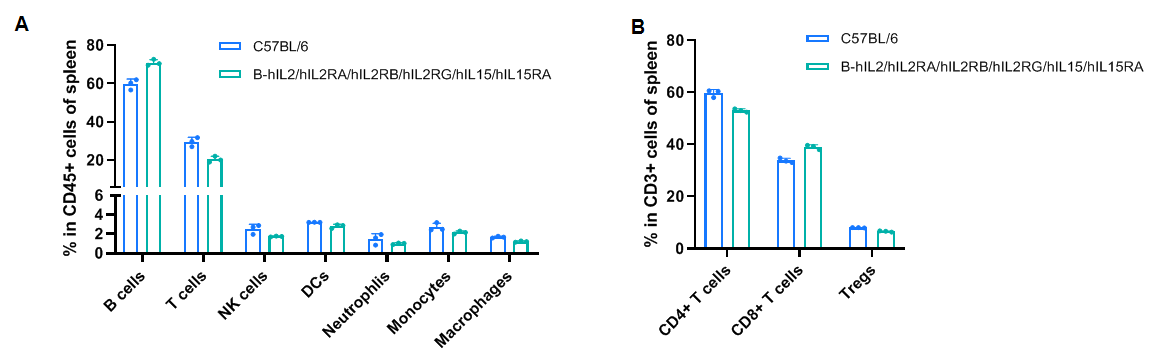
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the spleen by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were isolated from female wild-type C57BL/6 mice (n=3, 6-week-old) and homozygous B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice (n=3, 6-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. The percentages of T cells, B cells, NK cells, DCs, neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and Tregs in B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice were similar to those in C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that humanization of IL2, IL2RA, IL2RB, IL2RG, IL15, and IL15RA does not change the frequency or distribution of these cell types in spleen. The frequencies of leukocyte subpopulations in the blood, lymph nodes, and thymus of B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice were also comparable to wild-type C57BL/6 (Data not shown). Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
Intracellular phosphorylation of STAT5 analysis in splenocytes by flow cytometry. Splenocytes at 2x10^6/well (96-well plate) were treated with different concentrations of IL2 for 30 min. Cells were collected and assessed for pSTAT5 in the different immune cells. As shown in the figure, IL2 induced pSTAT5 in T cells and NK cells in a dose dependent manner; however, no pSTAT5 induction was observed in CD4+ T cells and Tregs.
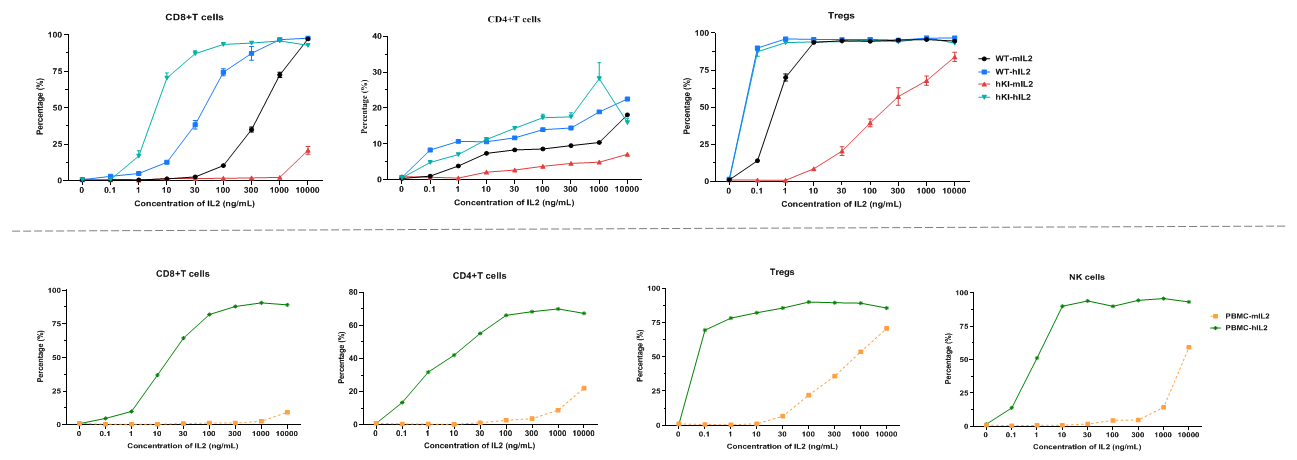
Intracellular phosphorylation of STAT5 analysis in splenocytes and human PBMC by flow cytometry. Splenocytes at 2 x 106/well (96-well plate) and human PBMC at 5 x 105/well (96-well plate) were treated with different concentrations of IL2 for 30 min, respectively. Cells were collected and assessed for pSTAT5 in the different immune cells. As shown in the figure, IL2 induced pSTAT5 in CD8+T cells, CD4+T cells, and Tregs in a dose dependent manner of both humanized mice and human PBMC. Further, the mouse IL2 could stimulate the B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice. However, the activation of mIL2 is weaker than that of hIL2.
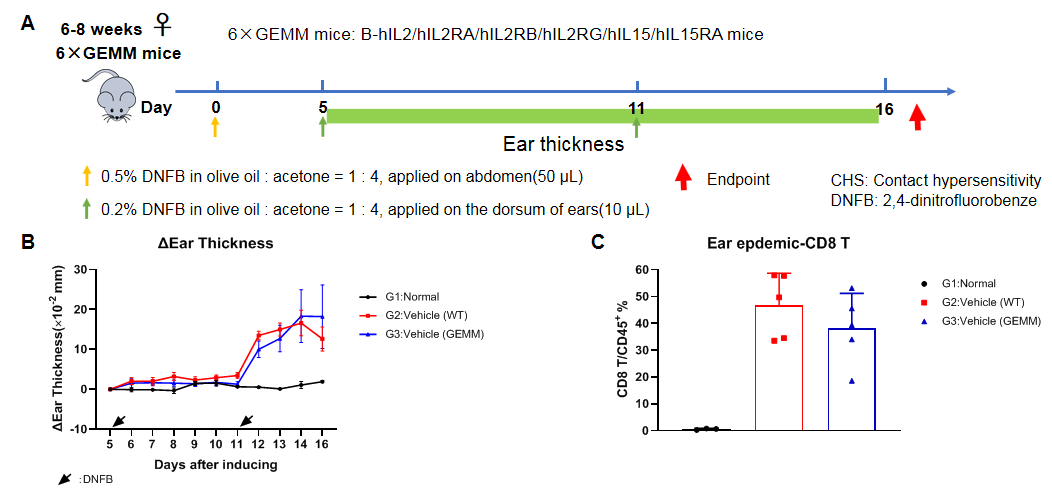
Exposure schedules and procedures for the DNFB-induced CHS model and analysis of characteristics in CHS model based on wild-type C57BL/6 and B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice. (A) The timeline of animal handling for the CHS experiment. (B) Change of ear thickness. (C) Frequency of CD8+ T cells within the ear epdemic site, determined by flow cytometry. The contact hypersensitivity(CHS) model can be established successfully in the B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice.
Note: This experiment was performed by the client using B-hIL2/hIL2RA/hIL2RB/hIL2RG/hIL15/hIL15RA mice. All the other materials were provided by the client.









