B-hCTLA4 mice(C)
| Strain Name | BALB/cCrSIcNifdc-Ctla4tm1(CTLA4)Bcgen/Bcgen | Common Name | B-hCTLA4 mice(C) |
| Background | BALB/cCrSIcNifdc | Catalog number |
112755 |
|
Aliases |
CTLA-4; ALPS5; GRD4; CTLA4; CD; CD152; IDDM12; GSE; CELIAC3 |
||
Description
- CTLA-4 (Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4) is a protein receptor that functions as an immune checkpoint and downregulates immune responses. It is expressed on the surface of Helper T cells and transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells. CTLA4 plays a critical role in maintaining immune homeostasis by preventing excessive or auto-reactive immune responses. Dysregulation of CTLA-4 function has been linked with autoimmune diseases and allergies. Moreover, cancer cells can exploit this pathway to evade the immune system, which has led to the development of anti-cancer immunotherapies targeting CTLA-41.
- Biocytogen developed an CTLA4 humanized mice, the exon 2 of mouse Ctla4 gene that encodes the extracellular domain was replaced by human CTLA4 exon 2 in B-hCTLA4 mice(C). Then, confirmed that human CTLA4 protein was exclusively detectable in T cell subtypes of homozygous B-hCTLA4 mice(C).
- The mice can be used for preclinical pharmacodynamics studies of target-related disease.
Protein expression analysis

Strain specific CTLA4 protein expression analysis in BALB/c mice and homozygous B-hCTLA4 mice(C) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild type BALB/c mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCTLA4 mice (H/H) that stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CTLA4 antibodies. Mouse CTLA4 was detectable in different T cell subtypes of wild-type BALB/c mice, while human CTLA4 was exclusively detectable in T cell subtypes of B-hCTLA4 mice(C) (H/H).
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in blood
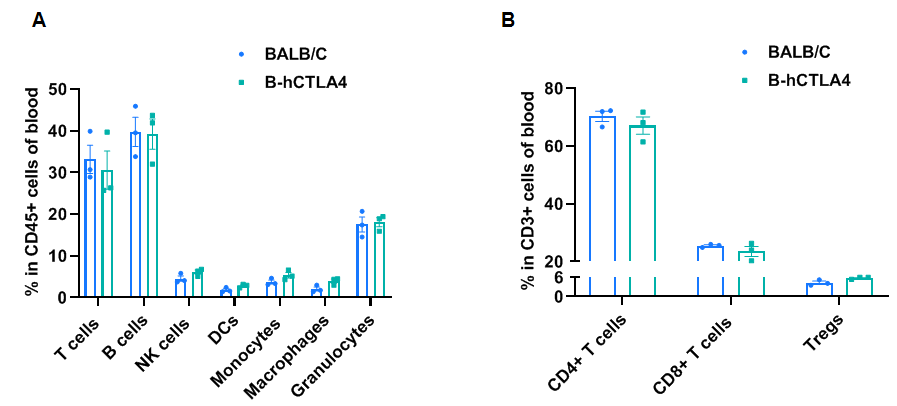
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in blood by flow cytometry. Blood cells were isolated from BALB/c and B-hCTLA4 mice(C) (n=3, 6-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the blood cells was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations in blood. Percentages of T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and Tregs in B-hCTLA4 mice were similar to those in BALB/c mice, demonstrating that humanization of CTLA4 does not change the frequency or distribution of these cell types in blood. The frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in thymus, lymph node and spleen of B-hCTLA4 mice were also comparable to wild-type BALB/C mice (Data not shown). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.









