B-hICOS(v2)/hICOSL mice
| Strain Name | C57BL/6-Icostm2(ICOS)Icosltm1(ICOSL)/Bcgen | Common Name | B-hICOS(v2)/hICOSL mice |
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number | 120542 |
|
Related Genes |
ICOS, ICOSL |
||
Inducible T-cell costimulator is an immune checkpoint protein that in humans is encoded by the ICOS gene. CD278 or ICOS (Inducible T-cell COStimulator) is a CD28-superfamily costimulatory molecule that is expressed on activated T cells. It is thought to be important for Th2 cells in particular). The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the CD28 and CTLA-4 cell-surface receptor family. It forms homodimers and plays an important role in cell-cell signaling, immune responses and regulation of cell proliferation.
ICOSL belongs to the B7 family of co-stimulatory molecules and shares sequence similarity with CD80 and CD86. ICOSL does not interact with CD28 or cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) despite its sequence homology with them, but rather binds to its receptor ICOS. Blocking ICOS-ICOSL interaction exacerbates experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, suggesting that its signaling negatively regulates unfavorable immune responses. In tumor microenvironments, Tregs protect tumors from immune cells.
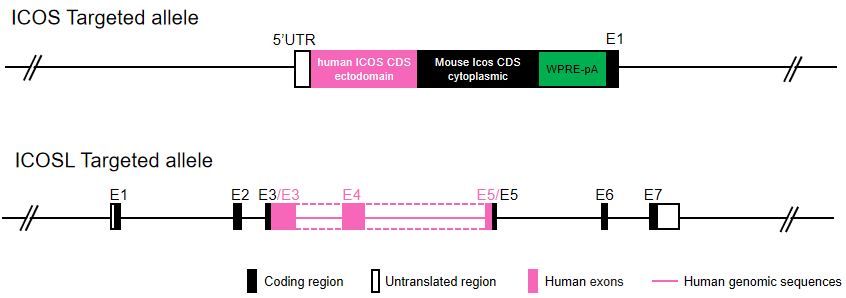
Gene targeting strategy for B-hICOS(v2)/hICOSL mice.
The human ICOS CDS that encode the extracellular domain were inserted in the mouse 5’UTR region.
The exons 3-5 of mouse Icosl gene that encode the extracellular domain were replaced by human ICOSL exons 3-5 in B-hICOS(v2)/hICOSL mice.
mRNA expression analysis

Strain specific analysis of ICOS and ICOSL gene expression in WT and hICOS(v2)/hICOSL mice by RT-PCR.
Mouse Icos and Icosl mRNA were detectable in splenocytes of wild-type (+/+) and heterozygous (H/+) mice. Human ICOS and ICOSL mRNA were detectable only in H/+ but not in +/+ mice.









