B-HLA-A3.1 mice
| Strain Name | C57BL/6JNifdc-B2mtm1(B2M/HLA-A3.1/H2-D)Bcgen/Bcgen | Common Name | B-HLA-A3.1 mice |
| Background | C57BL/6JNifdc | Catalog number |
113248 |
|
Aliases |
Ly-m11, beta2m, beta2-m | ||
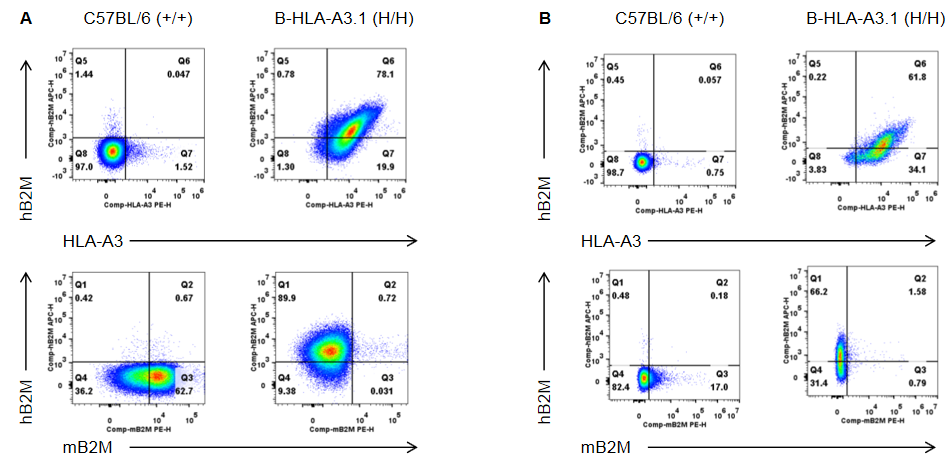
Strain specific B2M and HLA-A3 expression analysis in wild type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous humanized B-HLA-A3.1 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes(A) and blood(B) were collected from wild type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-HLA-A3.1 mice (H/H), respectively, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-HLA-A3 and anti-B2M antibody. HLA-A3 and human B2M were exclusively detectable in homozygous B-HLA-A3.1 mice.
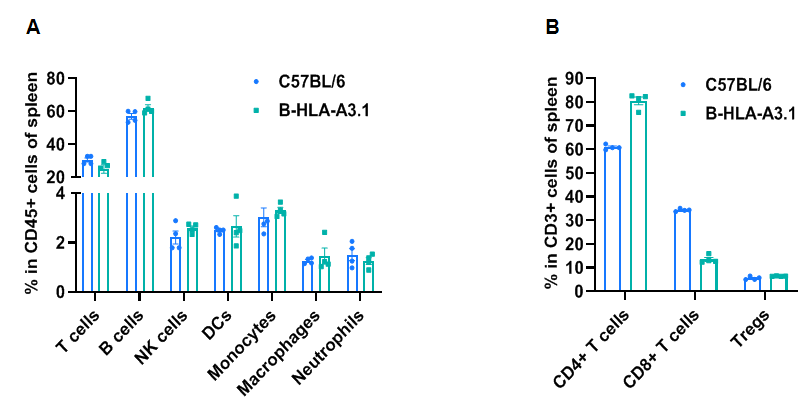
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in spleen by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were isolated from wild type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-HLA-A3.1 mice (n=4, 2 female and 2 male, 7-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. Percentages of T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages and Tregs in B-HLA-A3.1 mice were similar to those in C57BL/6 mice. Percent of CD8+ T cells were significantly decreased while percent of CD4+ T cells were significantly increased, demonstrating that introduction of hB2M-HLA-A3.1-H-2D in place of mouse B2M may affected the development of CD8 + T cells, which in turn affected the proportion of T cell subtypes in the spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Peptide vaccines induced immune responses in B-HLA-A3.1 mice

Detection of vaccine-induced immune responses in B-HLA-A3.1 mice by IFN-γ ELISpot assay. Female C57BL/6 mice and B-HLA-A3.1 mice at the age of 7–8 weeks were divided into PBS group and SART3 734-742 group (n = 3), and then inoculated PBS or vaccines at the inside muscle of both legs. Three weeks after the last immunization, mice were sacrificed. The splenocytes were extracted, stimulated with individual peptide or target-unrelated polypeptide as negative control (NC) or PMA/Ionomycin(R&D, 423302) as positive control(PC), and then measured for IFN-γ secretion. No significant difference in body weight among groups (Data was not shown). (A) Representative results showing stimulation of splenocytes harvested from immunized mice with negative control, peptide vaccines, or positive control in duplicates. (B) Summary of results. The results demonstrate that the SART3 734-742 can’t induce immune responses in B-HLA-3.1 because the HLA-A3.1 doesn’t recognize this peptide. NC: negative control, PC: positive control.

Detection of vaccine-induced immune responses in B-HLA-A3.1 mice by IFN-γ ELISpot assay. Female C57BL/6 mice and B-HLA-A3.1 mice at the age of 7–8 weeks were divided into PBS group and G12V 7-16 group (n = 3), and then inoculated PBS or vaccines at the inside muscle of both legs. Three weeks after the last immunization, mice were sacrificed. The splenocytes were extracted, stimulated with individual peptide or target-unrelated polypeptide as negative control (NC) or PMA/Ionomycin(R&D, 423302) as positive control(PC), and then measured for IFN-γ secretion. No significant difference in body weight among groups (Data was not shown). (A) Representative results showing stimulation of splenocytes harvested from immunized mice with negative control, peptide vaccines, or positive control in duplicates. (B) Summary of results. The results demonstrate that B-HLA-3.1 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of vaccines. NC: negative control, PC: positive control.









