B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice
| Strain Name |
C57BL/6-Slc3a2tm1(SLC3A2)Bcgen Mapttm1(MAPT*P301S)Bcgen/Bcgen |
Common Name | B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice |
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number |
113206 |
|
Related Genes |
4F2, 4F2HC, 4T2HC, CD98, CD98HC, MDU1, NACAE; TAU, MSTD, PPND, DDPAC, MAPTL, MTBT1, MTBT2, tau-40, FTDP-17, PPP1R103, Tau-PHF6 |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
6520, 4137 | ||
- TAU is mainly distributed in the central nervous system, most of it exists in the axons of neurons, and a small amount exists in oligodendrocytes. TAU is involved in neurodegenerative diseases, and most prominently in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease (AD).
- CD98HC is a transmembrane glycoprotein that plays a key role in amino acid transport and cell adhesion. Certain therapeutic drugs exploit the transport mechanism mediated by CD98HC to effectively cross the blood-brain barrier. This ability is especially important for the treatment of neurological disorders.
- Gene editing strategy: The full coding sequences of human TAU gene with P301S mutation that is driven by mouse Prnp promoter are inserted into mouse Hipp11 (H11) locus in B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice. The exons 2-10 of mouse Cd98 gene that encode the extracellular domain were replaced by human CD98 exons 4-12 in B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice.
- Protein expression analysis: TAU and p-tau were detected in cortex and hippocampus of both wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice. Additionally, homozygous B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice showed a significant increase in TAU and p-tau levels compared to wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human CD98HC was exclusively detectable on T cells and B cells of homozygous B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice, and mouse CD98 was detectable only in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
- Application: This product is used for pharmacodynamics evaluation of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Targeting strategy
Gene targeting strategy for B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice. The full coding sequences of human TAU gene with P301S mutation that is driven by mouse Prnp promoter are inserted into mouse Hipp11 (H11) locus in B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice. The exons 2-10 of mouse Cd98 gene that encode the extracellular domain were replaced by human CD98 exons 4-12 in B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice.
Protein expression analysis
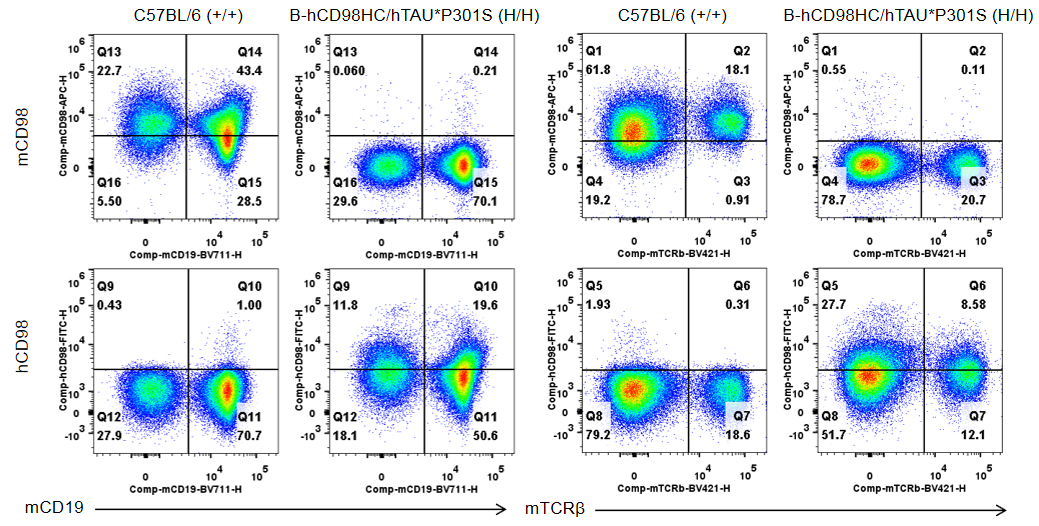
Strain specific CD98 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice (H/H), and analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-mouse CD98 antibody (Biolegend, 128211) and anti-human CD98HC antibody (Biolegend, 315603). Mouse CD98 was detectable in B cells and T cells form wild-type mice. Human CD98HC was exclusively detectable in B cells and T cells from homozygous B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice but not in wild-type mice.
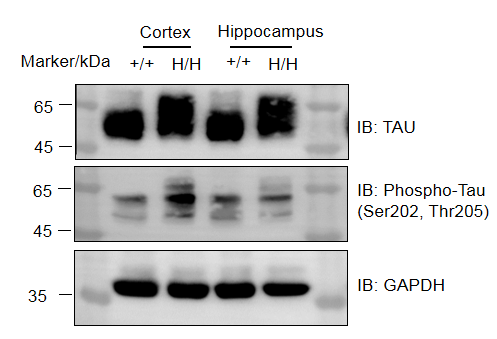
Western blot analysis of phosphorylation of TAU protein expression in homozygous B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice. Cortex and hippocampus lysates were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD98HC/hTAU*P301S mice (H/H, 6-week-old mice), and then analyzed by western blot (Phospho-Tau (Ser202, Thr205) antibody: Invitrogen, MN1020; anti-TAU antibody: CST, #46687). 40 μg total proteins were loaded for western blotting analysis. TAU and p-tau were detected in cortex and hippocampus of both wild-type and homozygous mice.









