B-hFIX mice
| Strain Name |
C57BL/6-F9tm1(F9)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-hFIX mice |
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number |
112829 |
|
Related Genes |
F9 p22, FIX, HEMB, P19, PTC, THPH8 |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
2158 | ||
- Factor IX, also known as Christmas Factor, is a 52 kDa zymogen of plasma serine proteases that initiates coagulation through activation by Tissue Factor (TF) and Factor VIIa. The activated form of Factor IX, known as Factor IXa, further activates an intrinsic activation complex that consists of factor X and factor VIIIa in the presence of Ca2+, and phospholipids. Mutations that cause a deficiency in Factor IX lead to x-linked hemophilia B, whereas overproduction of Factor IX has been shown to be a risk factor in venous thromboembolism (VTE).
- Factor IX (F9) is produced in liver cells and exists freely in the blood.
- The mouse F9 gene were replaced by full length human F9 exons 1~8 in B-hFIX mice, The promoter, 5'UTR and 3’UTR also use human sequences .
- Human FIX was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hFIX mice by ELISA.
- Mouse F9 mRNA was only detectable in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice. Human F9 mRNA was only detectable in homozygous B-hFIX mice.
- Application: This product is used for pharmacodynamics and safety evaluation of drugs. Can continue to knock out F8 to develop a hemophilia model.
Targeting strategy
- The exons 3~8 of mouse F9 gene were replaced by full length human F9 exons 1~8 in B-hFIX mice.
- The promoter and 5’UTR region of the mouse gene are retained, but they have no function anymore.
- The 3’UTR region of the mouse gene are replaced by 3’UTR region of human gene. The promoter, 5'UTR also use human sequences
mRNA expression analysis in humanized B-hFIX mice
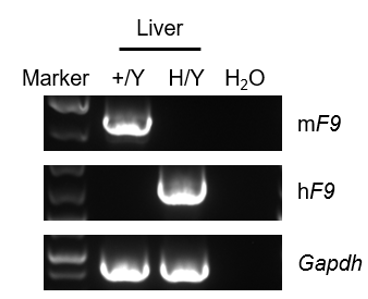
Strain specific analysis of FIX mRNA expression in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and B-hFIX mice by RT-PCR. Liver mRNA were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/Y) and homozygous B-hFIX mice (H/Y), then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by PCR with mouse or human FIX primers. Mouse F9 was detectable only in wild-type mice. Human FIX mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hFIX mice but not in wild-type mice.
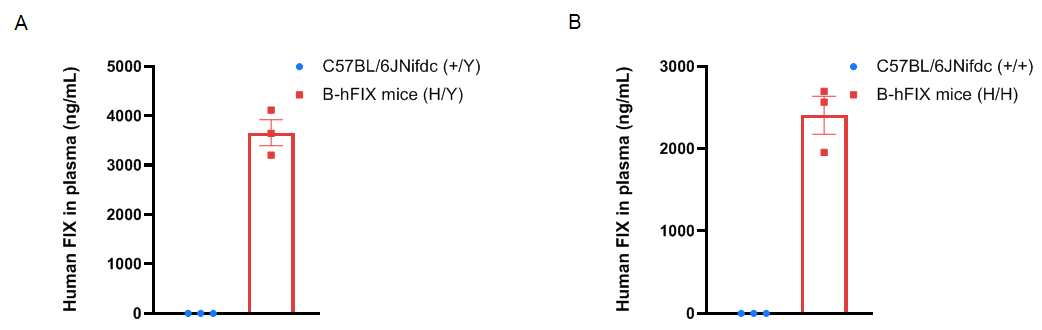
Strain specific FIX expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and homozygous humanized B-hFIX mice by ELISA. Plasma was collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (male, 9-week-old, n=3, +/Y; female, 11-week-old, n=3, +/+) and homozygous B-hFIX mice (male, 9-week-old, n=3, H/Y; female, 11-week-old, n=3, H/H). Protein expression level of FIX was analyzed by ELISA (Abcam, ab188393). Human FIX was exclusively detectable in male (A) and female (B) homozygous B-hFIX mice
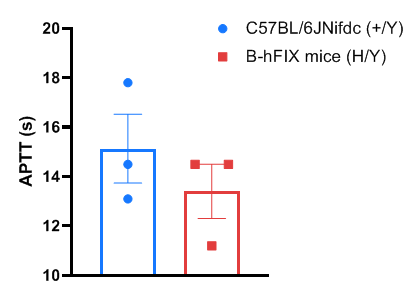
Blood coagulation analysis in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and homozygous humanized B-hFIX mice. Plasma was collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/Y) and homozygous B-hFIX mice (H/Y) (male, 9-week-old, n=3). There was no significant difference in APTT values between homozygous B-hFIX mice and wild-type mice. APTT: activated partial thromboplastin time.









