B-hNTS mice
| Strain Name |
C57BL/6N-Ntstm1(NTS)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-hNTS mice |
| Background | C57BL/6N | Catalog number |
112912 |
|
Related Genes |
NTS; NN, NT, NT/N, NTS1, NMN-125 |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
4922 | ||
- Neurotensin is a secreted tridecapeptide, which is widely distributed throughout the central nervous system, and may function as a neurotransmitter or a neuromodulator. It may be involved in dopamine-associated pathophysiological events, in the maintenance of gut structure and function, and in the regulation of fat metabolism.
- Neurotensin also exhibits antimicrobial activity against bacteria and fungi. Tissue-specific processing may lead to the formation in some tissues of larger forms of neuromedin N and neurotensin. The large forms may represent more stable peptides that are also biologically active.
Targeting strategy
Gene targeting strategy for B-hNTS mice. The exons 2-4 of mouse Nts gene, including 3’UTR were replaced by human counterparts in B-hNTS mice. The promoter, 5’UTR and signal peptide region of the mouse gene are retained. The human NTS expression is driven by endogenous mouse Nts promoter, while mouse Nts gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
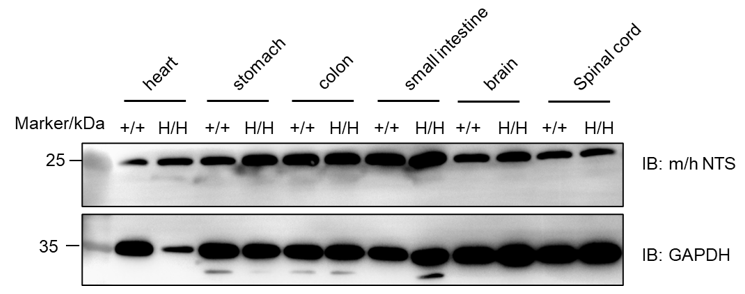
Western blot analysis of NTS protein expression in homozygous B-hNTS mice. Various tissue lysates were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hNTS mice (H/H), and then analyzed by western blot with anti-NTS antibody(abcam, ab233107). 40 μg total proteins were loaded for western blotting analysis. NTS was detected in heart, stomach, colon, small intestine and spinal cord.
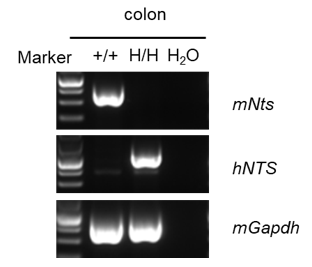
Strain specific analysis of NTS mRNA expression in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and B-hNTS mice by RT-PCR. Colon RNA were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hNTS mice (H/H), then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by PCR with mouse or human NTS primers. Mouse Nts mRNA were detectable only in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human NTS mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hNTS mice but not in wild-type mice.









