B-hMERTK MC38
|
Common name |
B-hMERTK MC38 | Catalog number | 311600 |
| Aliases | MER, RP38, Tyro12, c-Eyk, c-mer | Disease | Colon carcinoma |
|
Organism |
Mouse |
Strain | C57BL/6 |
| Tissue types | Colon | Tissue | Colon |
Description
The exogenous promoter and chimeric MERTK coding sequence containing human signal peptide, extracellular domain, transmembrane domain and mouse cytoplasmic domain was inserted to replace part of murine exon 1.
B-hMERTK MC38 cells have the capability to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies.
Gene targeting strategy for B-hMERTK MC38 cells. The exogenous promoter and chimeric MERTK coding sequence containing human signal peptide, extracellular domain, transmembrane domain and mouse cytoplasmic domain was inserted to replace part of murine exon 1. The insertion disrupts the endogenous murine Mertk gene, resulting in a non-functional transcript.
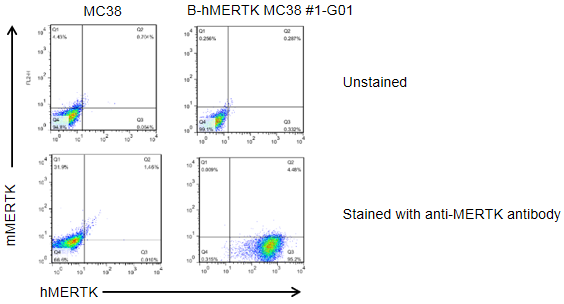
MERTK expression analysis in B-hMERTK MC38 cells by flow cytometry. Single cell suspensions from wild-type MC38 and B-hMERTK MC38 cultures were stained with species-specific anti-MERTK antibody. Human MERTK was detected on the surface of B-hMERTK MC38 cells but not wild-type MC38 cells. The 1-G01 clone of B-hMERTK MC38 cells was used for in vivo experiments.
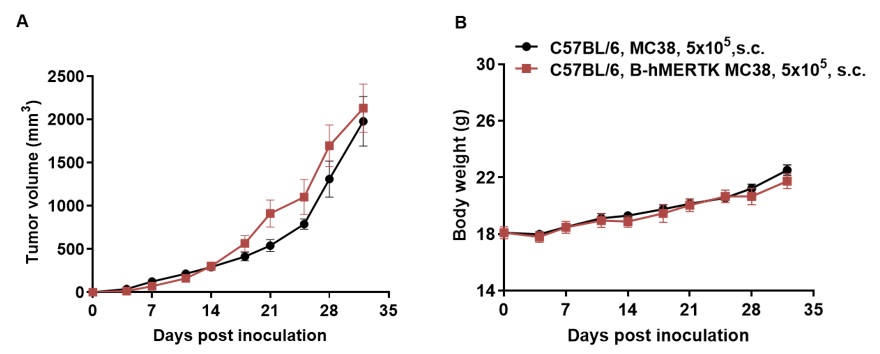
Subcutaneous homograft tumor growth of B-hMERTK MC38 cells. B-hMERTK MC38 cells (5x105) and wild-type MC38 cells (5x105) were subcutaneously implanted into C57BL/6 mice (female, 7-week-old, n=5). Tumor volume and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Average tumor volume ± SEM. (B) Body weight (Mean± SEM). Volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula: V=0.5 X long diameter X short diameter2. As shown in panel A, B-hMERTK MC38 cells were able to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies.
Tumor growth curve of individual mice
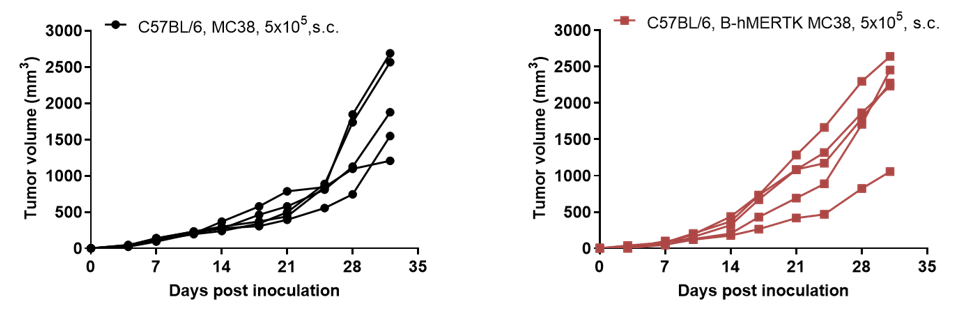
B-hMERTK MC38 tumor cells growth of individual mice. B-hMERTK MC38 cells (5x105) and wild-type MC38 cells (5x105) were subcutaneously implanted into C57BL/6 mice (female, 7-week-old, n=5). As shown in panel, B-hMERTK MC38 cells were able to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies.
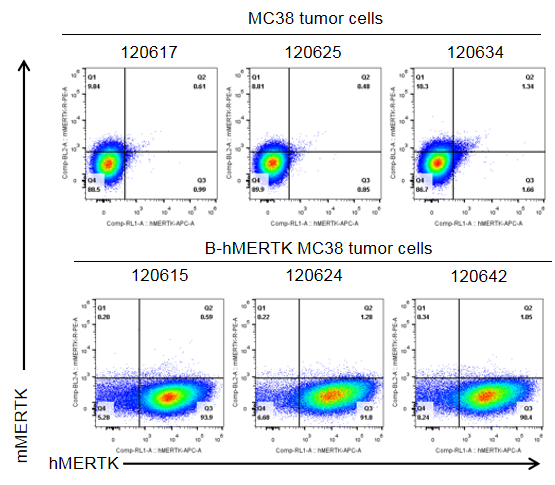
B-hMERTK MC38 cells were subcutaneously transplanted into C57BL/6 mice (n=5). At the end of the experiment, tumor cells were harvested and assessed for human MERTK expression by flow cytometry. As shown, human MERTK was highly expressed on the surface of tumor cells. Therefore, B-hMERTK MC38 cells can be used for in vivo efficacy studies of novel MERTK therapeutics.









