B-hRHO*P23H mice
| Strain Name |
C57BL/6JNifdc-Rhotm1(RHO*P23H)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-hRHO*P23H mice |
| Background | C57BL/6JNifdc | Catalog number | 113150 |
|
Aliases |
CSNBAD1, OPN2, RP4 |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
6010 | ||
- RHO, a G protein-coupled receptor protein possessing seven transmembrane domains, is situated in the outer segments of rods and plays a crucial role in enabling vision under dim light conditions. Mutations in the Rhodopsin (RHO) gene represent a major contributor to autosomal dominant RP (adRP), constituting 25%–30% of all adRP cases. In the human RHO gene, there exist more than 150 mutations, among which the RHO-P23H mutation (c.68C>A; p.Pro23His) is the most prevalent. In contrast to WT C57BL/6 or hRHOWT/WT mice, the photoreceptors of the or hRHOP23H/WT mouse model degenerated gradually over time after birth.
- Gene targeting strategy for B-hRHO*P23H mice. The promoter and 5’UTR region, the exons 1-5 of mouse Rho gene that encode signal peptide, extracellular domain, transmembrane domain, cytoplasmic region and 3’UTR are replaced by human counterparts with p.P23H(CCC to CAC)mutation in B-hRHO*P23H mice. The human RHO expression is driven by human RHO promoter, while mouse Rho gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
- Mouse Rho mRNA was detectable in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice. Human RHO*P23H mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hRHO*P23H mice but not in wild-type mice.
- The photoreceptor outer segments, outer nuclear layers, outer plexiform layers, and inner nuclear layers became thinner in B-hRHO*P23H mice compared with C57BL/6JNifdc mice.
Targeting strategy
Gene targeting strategy for B-hRHO*P23H mice. The promoter and 5’UTR region, the exons 1-5 of mouse Rho gene that encode signal peptide, extracellular domain, transmembrane domain, cytoplasmic region and 3’UTR are replaced by human counterparts with p.P23H(CCC to CAC)mutation in B-hRHO*P23H mice. The human RHO expression is driven by human RHO promoter, while mouse Rho gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
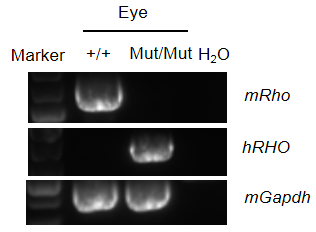
Strain-specific analysis of RHO*P23H mRNA expression in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and humanized B-hRHO*P23H mice by RT-PCR. Eye RNA was isolated from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hRHO*P23H mice (Mut/Mut), then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by PCR with mouse Rho or human RHO primers. Mouse Rho mRNA was detectable in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice. Human RHO mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hRHO*P23H mice but not in wild-type mice. And the position of the point mutation of RHO*P23H was correct.
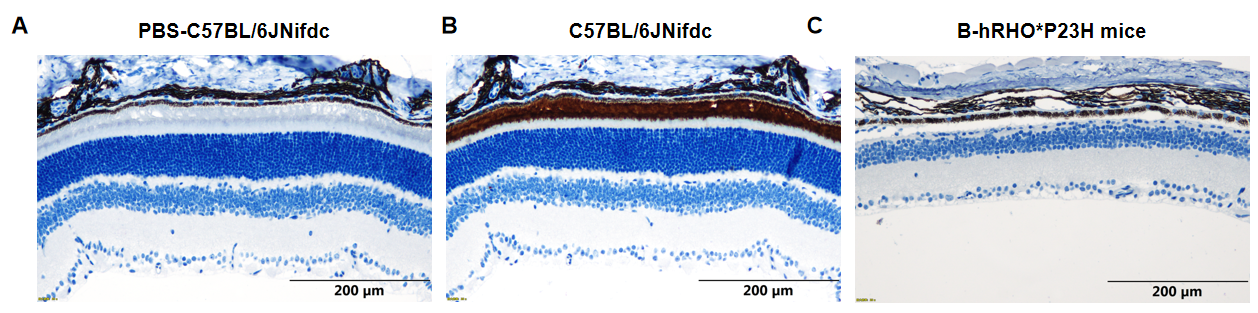
Representative images of RHO expression in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and B-hRHO*P23H mice. Retina tissues of wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+) and B-hRHO*P23H mice (Mut/Mut) (n=3, 5 weeks old, male) were collected and analyzed with IHC staining (abcam, ab221664), retina of wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice stained with PBS was tissue-negative control (A). Compared with wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice, the outer nuclear layer (ONL) of homozygous B-hRHO*P23H mice was thinner, and the expression of rhodopsin protein on the retina was abnormal (B-C). Scale bar, 200 mm.

Representative images of HE staining of wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and heterozygous B-hRHO*P23H mice. Retina tissues of wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+) and B-hRHO*P23H mice (Mut/+) (n=3, 12 weeks old, female) were collected and analyzed with H&E staining. The results showed that the photoreceptors of heterozygous B-hRHO*P23H mice degenerated compared to the C57BL/6JNifdc mice. The photoreceptor outer segments, outer nuclear layers, outer plexiform layers, and inner nuclear layers became thinner in B-hRHO*P23H mice compared with C57BL/6JNifdc mice.
OS, outer segment; ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. Scale bar, 200 mm.
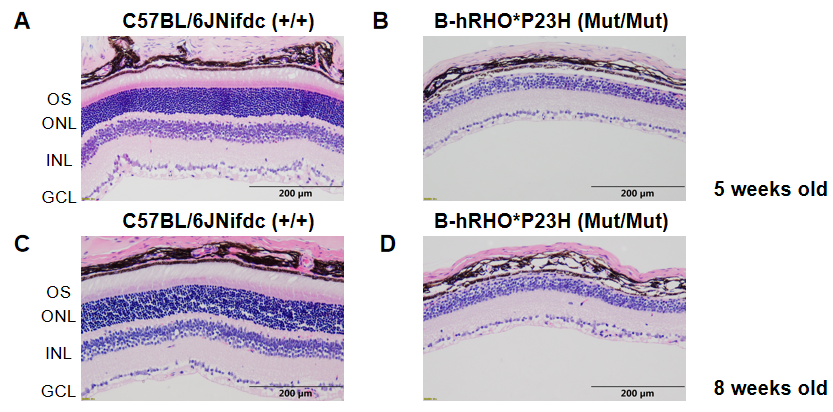
Representative images of HE staining of wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and homozygous B-hRHO*P23H mice. Retina tissues of wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+) and B-hRHO*P23H mice (Mut/Mut) (n=3, 5 weeks old and 8 weeks old, male) were collected and analyzed with H&E staining. The results showed that the photoreceptors of homozygous B-hRHO*P23H mice degenerated compared to the C57BL/6JNifdc mice. The photoreceptor outer segments, outer nuclear layers, outer plexiform layers, and inner nuclear layers became thinner in B-hRHO*P23H mice compared with C57BL/6JNifdc mice.
OS, outer segment; ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. Scale bar, 200 mm.









